Hydraulic Piston Seal Design Considerations for High-Pressure Applications
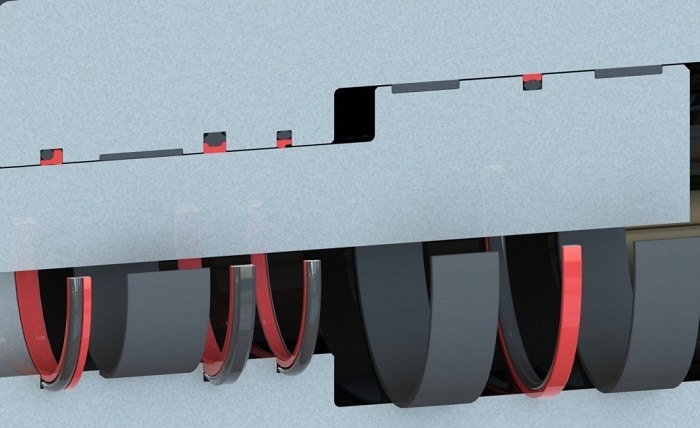
Hydraulic piston seals play a crucial role in the efficient and reliable operation of hydraulic systems, especially in high-pressure applications. These seals are responsible for containing hydraulic fluid within the cylinder, preventing leakage and ensuring optimal performance. In high-pressure environments, the design and selection of piston seals become critical factors in maintaining system integrity and functionality. In this article, we delve into the key considerations for designing hydraulic piston seal for high-pressure applications, ensuring durability, efficiency, and minimal downtime. Additionally, we’ll explore the relevance of mobile compactors in managing waste generated in hydraulic system maintenance.
Understanding High-Pressure Hydraulic Systems
High-pressure hydraulic systems are commonly used in a variety of industrial and mobile applications, including heavy machinery, construction equipment, aerospace systems, and more. These systems operate under extreme conditions, exerting significant force to perform tasks such as lifting, pressing, and moving heavy loads. The hydraulic piston seal within these systems must withstand the intense pressures and dynamic forces encountered during operation.
Key Design Considerations for High-Pressure Hydraulic Piston Seals
- Material Selection:
– The choice of seal material is paramount in high-pressure applications. Materials must exhibit excellent resistance to abrasion, extrusion, and wear.
– Common materials include polyurethane, nitrile rubber (NBR), fluorocarbon (Viton), and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE).
– For extreme conditions, specialized materials such as high-performance thermoplastics or elastomers may be required.
- Pressure Rating:
– Hydraulic piston seals for high-pressure systems must have a suitable pressure rating to withstand the forces exerted.
– The seal’s material composition, thickness, and design geometry determine its ability to withstand pressure without failure.
– Pressure ratings are typically specified in units such as PSI (pounds per square inch) or bar.
- Seal Geometry and Profile:
– The seal’s geometry plays a crucial role in its ability to maintain sealing integrity under pressure.
– Considerations include lip geometry, cross-sectional shape (e.g., O-ring, U-cup, V-ring), and contact pressure distribution.
– Properly designed seals distribute pressure evenly across the sealing surface, reducing the risk of seal deformation or extrusion.
- Compression Set Resistance:
– Hydraulic piston seals must maintain their sealing properties over extended periods without permanent deformation.
– Compression set resistance refers to the seal’s ability to return to its original shape after being compressed.
– Materials with low compression set properties ensure long-term sealing performance in high-pressure environments.
- Fluid Compatibility:
– Compatibility with hydraulic fluids is critical to prevent seal degradation and swelling.
– The seal material must resist chemical attack and breakdown when exposed to hydraulic fluids, including mineral oils, synthetic fluids, and water-based solutions.
– Compatibility testing ensures that the seal material remains stable and functional over the system’s operational life.
- Temperature Resistance:
– High-pressure hydraulic systems often operate in environments with wide temperature variations.
– Hydraulic piston seals should maintain their sealing properties across a broad temperature range, from extreme cold to high heat.
– Materials with excellent thermal stability and resistance to temperature fluctuations are ideal for high-pressure applications.
- Seal Lubrication:
– Proper lubrication is essential for reducing friction, wear, and heat generation within the seal interface.
– Lubricants help maintain seal flexibility, prevent drying out, and extend the seal’s operational life.
– Compatibility between the seal material and lubricant is crucial to prevent degradation or loss of sealing effectiveness.
- Dynamic Sealing Performance:
– In high-pressure applications, hydraulic piston seals experience dynamic movements as the piston reciprocates.
– The seal design should account for dynamic sealing performance, minimizing friction, and ensuring smooth operation.
– Features such as reinforced lips, anti-extrusion rings, and energizing elements enhance the seal’s ability to maintain a tight seal during movement.
- Installation and Assembly:
– Proper installation procedures are critical to the seal’s effectiveness and longevity.
– Seals should be installed with the correct orientation, ensuring that lip seals properly engage with the cylinder walls.
– Careful handling during assembly prevents damage to the seal and maintains its integrity under pressure.
Role of Mobile Compactors in Hydraulic System Maintenance
Mobile compactors play a crucial role in managing the waste generated during hydraulic system maintenance, including the replacement of hydraulic piston seals. These compactors offer the following benefits:
- Efficient Waste Compaction:
– Mobile compactors efficiently compress waste materials, including used seals, packaging, and other debris.
– Compacted waste takes up significantly less space, reducing the frequency of waste disposal and transportation.
- Space Optimization:
– By compacting waste into dense units, mobile compactors optimize storage space within the maintenance facility.
– This frees up valuable floor space and ensures a clean and organized working environment.
- Environmental Sustainability:
– Proper waste management with mobile compactors promotes environmental sustainability by reducing landfill waste.
– Compacted waste is easier to transport and dispose of responsibly, minimizing the impact on the environment.
- Cost Savings:
– Mobile compactors result in cost savings by reducing waste disposal costs and the need for frequent waste pickups.
– Efficient waste management practices contribute to overall operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
- Convenience and Safety:
– Mobile compactors offer a convenient and safe solution for managing waste on-site.
– Operators can easily load waste materials into the compactor, reducing manual handling and the risk of injuries.
Conclusion
Designing hydraulic piston seals for high-pressure applications requires careful consideration of various factors, including material selection, pressure rating, seal geometry, and fluid compatibility. These seals must withstand extreme forces, temperature variations, and dynamic movements while maintaining optimal sealing integrity. Properly designed and selected seals ensure efficient and reliable operation of high-pressure hydraulic systems, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
Additionally, mobile compactors play a vital role in managing waste generated during hydraulic system maintenance. These compactors offer efficient waste compaction, space optimization, environmental sustainability, cost savings, and enhanced convenience and safety. By integrating proper seal design and efficient waste management practices, operators can optimize the performance and longevity of high-pressure hydraulic systems while minimizing their environmental footprint.




