Classification of Computers: A Comprehensive Guide
Computers have become an integral part of our daily lives, whether for personal use, business, or scientific research. The classification of computers is essential for understanding the diverse functions they serve. Computers can be categorized based on their size, purpose, and functionality. This blog will explore the classification of computers, detailing the different types and their roles in various industries.
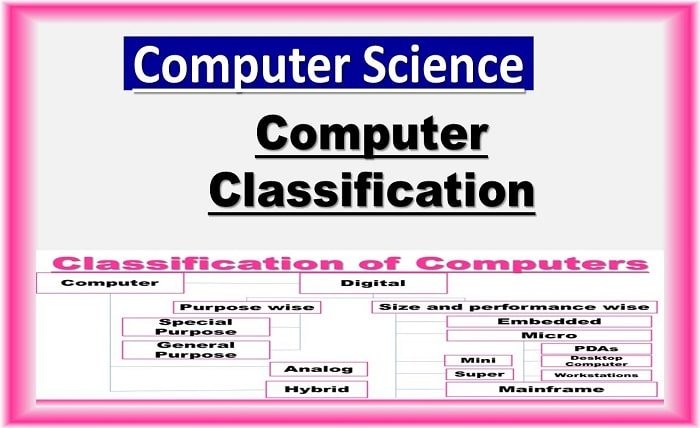
The Classification of Computers
The classification of computers is vital for identifying their specific roles in society. Computers come in various forms and sizes, each designed to perform particular tasks. From the massive supercomputers that process complex scientific data to personal computers that handle everyday tasks, understanding the classification of computers helps us appreciate their technological evolution.
Classification of Computers Based on Size
One way to categorize computers is by their size. This classification of computers includes categories such as supercomputers, mainframe computers, minicomputers, and microcomputers.
- Supercomputers: The most powerful type of computers, supercomputers are used for large-scale scientific computations, weather forecasting, and simulations.
- Mainframe Computers: Mainframe computers are designed for large organizations, managing massive amounts of data and supporting numerous users simultaneously.
- Minicomputers: Smaller than mainframes but more powerful than personal computers, minicomputers are used in mid-sized businesses for tasks like database management.
- Microcomputers: Commonly referred to as personal computers, microcomputers include desktops, laptops, and tablets, designed for individual users.
Classification of Computers Based on Functionality
The classification of computers can also be done based on their functionality. Depending on the tasks they perform, computers can be categorized into general-purpose and special-purpose computers.
- General-Purpose Computers: These computers are designed to perform a wide range of tasks, such as personal computing, business applications, and gaming. Personal computers and laptops fall under this category.
- Special-Purpose Computers: These computers are designed for specific tasks. Examples include embedded systems in cars or medical devices, which perform dedicated functions without flexibility.
Analog, Digital, and Hybrid Computers
Another classification of computers is based on the type of data they process. This leads to three distinct categories: analog computers, digital computers, and hybrid computers.
- Analog Computers: Analog computers process continuous data and are often used in scientific and engineering fields. They simulate complex processes such as electrical signals.
- Digital Computers: Digital computers process discrete data in binary format (0s and 1s) and are used for most of today’s applications, from smartphones to servers.
- Hybrid Computers: Combining the features of both analog and digital computers, hybrid computers are used in specialized applications like medical diagnostics and scientific research.
Classification of Computers by Purpose
The classification of computers can also depend on their purpose, whether for personal use, business, or research.
- Personal Computers (PCs): Designed for individual use, personal computers are used in homes and small offices for tasks like word processing, browsing, and multimedia.
- Workstations: More powerful than PCs, workstations are used for technical applications such as computer-aided design (CAD), scientific simulations, and complex data analysis.
- Servers: Servers manage network resources and are crucial in large businesses, handling tasks such as file storage, email, and database management.
- Supercomputers and Mainframes: As mentioned earlier, these are used for specialized tasks in large-scale businesses and scientific research.
Portable Computers
In the modern era, portability is a key factor in the classification of computers. Portable computers like laptops, notebooks, tablets, and smartphones have revolutionized how we work and communicate.
- Laptops and Notebooks: These portable computers offer similar functionality to desktop computers but come in a compact form, making them ideal for business professionals and students.
- Tablets: Tablets bridge the gap between smartphones and laptops, offering touch-based interfaces and portability while retaining enough processing power for various tasks.
- Smartphones: Smartphones are essentially handheld computers with extensive processing power, used for communication, entertainment, and productivity.
Classification of Computers Based on Architecture
The internal structure and architecture also contribute to the classification of computers. The most common architectures include the von Neumann and Harvard architectures.
- Von Neumann Architecture: This architecture uses a single storage structure for both data and instructions, leading to a more flexible system. It’s the foundation of most modern computers.
- Harvard Architecture: Harvard architecture, used in some embedded systems, separates storage for data and instructions, making it more efficient for certain tasks.
Real-Time Computers
The classification of computers also extends to real-time systems, which are designed to provide immediate processing and feedback.
- Hard Real-Time Systems: These computers are used in critical systems where any delay can result in failure, such as in medical equipment or aircraft control systems.
- Soft Real-Time Systems: These systems allow for some flexibility in response time and are often found in applications like multimedia systems.
Distributed and Networked Computers
Distributed computing systems represent another aspect of the classification of computers. In these systems, computers are connected via networks to perform collaborative tasks.
- Distributed Computing Systems: In these systems, multiple computers work together to solve complex problems, each contributing processing power.
- Networked Computers: Networked computers communicate with each other to share resources and data. Examples include local area networks (LANs) and wide area networks (WANs).
Classification of Computers in Cloud Computing
The rise of cloud computing has added a new dimension to the classification of computers. In cloud computing, resources are delivered over the internet, and the physical location of computing hardware becomes less relevant.
- Public Cloud: In a public cloud, resources are shared among multiple users, and computing power is provided as a service by third-party providers.
- Private Cloud: A private cloud is used exclusively by a single organization, offering more control and security over the computing environment.
- Hybrid Cloud: Hybrid cloud systems combine elements of both public and private clouds, offering flexibility and scalability for various applications.
Conclusion
The classification of computers is essential for understanding the vast array of devices and systems that exist today. From powerful supercomputers driving scientific research to portable smartphones enabling global communication, computers serve diverse functions in every aspect of modern life. This classification system helps us appreciate the capabilities of each type and how they contribute to technological progress.
FAQs
1. What is the classification of computers based on size?
The classification of computers based on size includes supercomputers, mainframe computers, minicomputers, and microcomputers. Each serves a different function depending on its size and processing power.
2. What are special-purpose computers?
Special-purpose computers are designed to perform specific tasks. Examples include embedded systems used in medical devices, cars, and industrial machinery.
3. How are computers classified based on functionality?
Computers are classified into general-purpose and special-purpose based on their functionality. General-purpose computers can perform a wide range of tasks, while special-purpose computers are designed for specific functions.
4. What is a hybrid computer?
A hybrid computer combines the features of both analog and digital computers, often used in specialized applications like medical diagnostics.
5. What are real-time computers?
Real-time computers are systems designed to provide immediate processing and response. They are classified into hard real-time systems (used in critical applications) and soft real-time systems (used in less time-sensitive applications).




