India is a vast and diverse country with a population of over 1.3 billion people. India is also a country with a high degree of urbanization, with more than 34% of its population living in urban areas. India has a complex and dynamic system of classifying its cities based on various criteria, such as population, economic activity, infrastructure, culture, and governance. One of the most common and popular classifications of Indian cities is the tier system, which divides the cities into four categories: Tier 1, Tier 2, Tier 3, and Tier 4. We will focus on the Tier 1 cities in India: what are they, how many are there, what are their characteristics, and why are they important?
What are Tier 1 Cities in India?
Tier 1 cities in India are the cities that have the highest population, economic activity, infrastructure, culture, and governance among all the cities in the country. Tier 1 cities are also known as X cities or metropolitan cities, as they serve as the major hubs of commerce, industry, education, entertainment, and politics in India. Tier 1 cities are also the most cosmopolitan and globalized cities in India, attracting people from different regions, states, and countries.
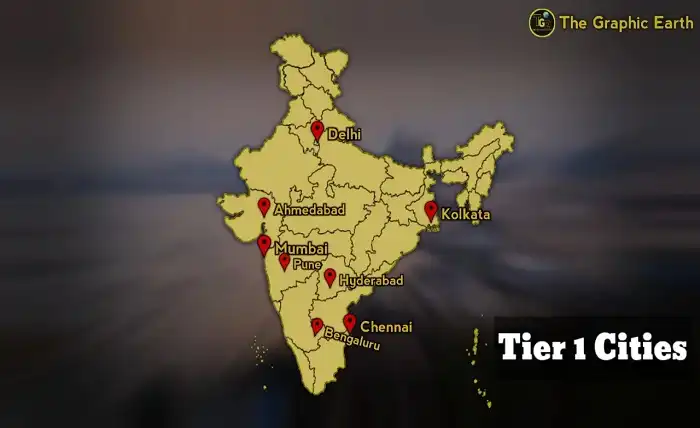
According to the classification of Indian cities by the Government of India for the purpose of allocating House Rent Allowance (HRA) to public servants employed in different cities, there are eight Tier 1 cities in India as of 2020. These are:
- Bengaluru
- Delhi
- Chennai
- Hyderabad
- Mumbai
- Pune
- Kolkata
- Ahmedabad
These eight cities are considered as India’s “metros” and have a population of more than four million each. These cities also have a high per capita income, a high literacy rate, a high human development index, and a high quality of life compared to other Indian cities.
What are the Characteristics of Tier 1 Cities in India?
Tier 1 cities in India have some common characteristics that distinguish them from other Indian cities. Some of these characteristics are:
- Economic Activity: Tier 1 cities in India are the engines of economic growth and development in the country. They contribute to more than 40% of India’s GDP and account for more than 70% of India’s foreign direct investment (FDI). They also have a diverse and dynamic economic base, ranging from manufacturing to services to information technology to biotechnology. They also have a large and skilled workforce, a vibrant entrepreneurial culture, and a strong presence of multinational corporations.
- Infrastructure: Tier 1 cities in India have a well-developed and modern infrastructure that supports their economic activity and urban lifestyle. They have a network of roads, railways, airports, ports, metro systems, bus rapid transit systems, and other modes of public transport that facilitate mobility and connectivity. They also have a supply of electricity, water, sanitation, telecommunication, and other utilities that ensure efficiency and reliability. They also have a range of social infrastructure, such as schools, colleges, universities, hospitals, malls, cinemas, parks, and other amenities that cater to the needs and aspirations of their residents.
- Culture: Tier 1 cities in India have a rich and diverse culture that reflects their history, heritage, and identity. They have a blend of traditional and modern values, beliefs, and practices that shape their social norms and behaviors. They also have a variety of languages, religions, cuisines, arts, music, literature, and festivals that celebrate their diversity and unity. They also have a vibrant and dynamic media, entertainment, and sports industry that influences their popular culture and lifestyle.
- Governance: Tier 1 cities in India have a complex and multi-layered governance structure that involves various stakeholders and institutions. They have a municipal corporation or council that is responsible for providing basic civic services and amenities to their residents. They also have a state government that is responsible for providing policy direction and financial support to their development. They also have a central government that is responsible for providing strategic guidance and coordination to their growth. They also have various civil society organizations, private sector entities, and citizens groups that participate in their governance process.
Read more about Adani Power Share: A High-Growth Stock with a Sustainable Vision
Why are Tier 1 Cities in India Important?
Tier 1 cities in India are important for various reasons,
such as:
- Economic Growth: Tier 1 cities in India are the drivers of economic growth and development in the country. They generate employment, income, and wealth for their residents and contribute to the national economy. They also attract investment, innovation, and entrepreneurship from within and outside the country. They also create opportunities for trade, commerce, and tourism with other countries.
- Social Development: Tier 1 cities in India are the centers of social development and empowerment in the country. They provide education, health, and other services to their residents and improve their human capital and well-being. They also promote social inclusion, equity, and justice for their diverse and marginalized communities. They also foster social cohesion, harmony, and peace among their different groups and cultures.
- Environmental Sustainability: Tier 1 cities in India are the leaders of environmental sustainability and resilience in the country. They adopt green and clean technologies and practices to reduce their carbon footprint and environmental impact. They also conserve and manage their natural resources and ecosystems to enhance their ecological health and biodiversity. They also mitigate and adapt to the effects of climate change and natural disasters to protect their people and assets.
- Global Influence: Tier 1 cities in India are the representatives of global influence and competitiveness in the country. They showcase their achievements, challenges, and potentials to the world and enhance their image and reputation. They also participate in global networks, partnerships, and initiatives to share their knowledge, experience, and best practices. They also influence and shape the global agenda and discourse on various issues and challenges.
Conclusion
Tier 1 cities in India are the cities that have the highest population, economic activity, infrastructure, culture, and governance among all the cities in the country. Tier 1 cities are also known as X cities or metropolitan cities, as they serve as the major hubs of commerce, industry, education, entertainment, and politics in India. Tier 1 cities are also the most cosmopolitan and globalized cities in India, attracting people from different regions, states, and countries.
According to the classification of Indian cities by the Government of India for the purpose of allocating House Rent Allowance (HRA) to public servants employed in different cities, there are eight Tier 1 cities in India as of 2020. These are Bengaluru, Delhi, Chennai, Hyderabad, Mumbai, Pune, Kolkata, and Ahmedabad. These eight cities have some common characteristics that distinguish them from other Indian cities, such as economic activity, infrastructure, culture, and governance.
Tier 1 cities in India are important for various reasons, such as economic growth, social development, environmental sustainability, and global influence. They contribute to the national economy, provide services and amenities to their residents, adopt green and clean technologies and practices, and participate in global networks and partnerships.