Keywords: managed services, managed wifi system
Until a few years ago, the only decision a digital or IT-oriented company had to make was choosing between cloud and on-premise software. But with the advent of cloud and its as-a-service offering, several use cases and platforms have come on the forefront.
All of these are making it difficult for companies to keep up. This article is a way to give you clarity around all the jargons and help you finalize the best approach in your digitalization journey.
The four major as-a-service managed services models that we are going to cover today include –
Infrastructure-as-a-Service
Software-as-a-Service
Platform-as-a-Service
Network-as-a-Service.
Let’s look into them in detail.
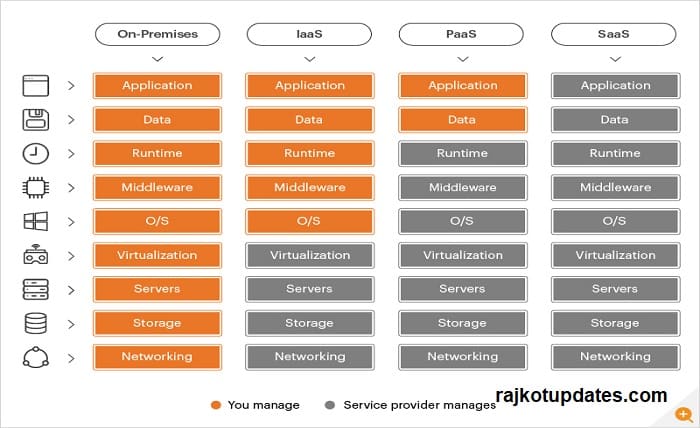
Infrastructure-as-a-Service
Infrastructure as a Service (or IaaS) is another/new name for “enterprise cloud.” Instead of ordering servers, giving time for it to get configured and connected, businesses can simply rent servers on the cloud.
Being an extensive full-range offering, IaaS tends to merge storage, computation, and networking on demand, in a way that the users are charged on a pay-as-you-go basis. Some of the top examples of IaaS include – Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Google Cloud.
IaaS is generally preferred by companies having dynamic networking requirements. Companies active in entertainment, retail, and sports tend to have certain network needs that change swiftly and whose IT teams could use a solution which combines all networking in one, extensible offering.
Use cases of the platform includes –
- Testing and development
- Hosting platforms
- Extensive data storage and backup
- Computation of capacity and data warehousing.
When to use IaaS?
Businesses need Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) to offload the burden of managing physical infrastructure such as servers, storage, and networking equipment. By leveraging IaaS, companies can scale resources up or down as needed, reduce capital expenditures, and benefit from increased flexibility and agility in deploying applications and services.
Platform-as-a-Service
Platform as a Service (PaaS) help companies bring development and delivery to the cloud. The platforms help businesses deliver everything from low-complex cloud-based services to complicated enterprise apps. What works for them is that companies are able to select the resource they require from a PaaS solution provider on a subscription level.
Similar to IaaS, PaaS comprises infrastructure such as computation, storage and networks. The platform supports the entire software development lifecycle: Building, testing, deploying, and managing.
PaaS is usually recommended for startups and small-scaled businesses. For businesses that work on digital transformation of their legacy systems or require a better approach to handle their remote workforce, PaaS offers a direct, urgent-level access to the best resources minus any heavy price tag.
Use cases of the as-a-service model can include –
- App development and testing
- Business Intelligence and business analysis
- Database management
- Process and task automation
When to use PaaS
Platform as a Service (PaaS) is essential for businesses looking to streamline their application development and deployment processes. With PaaS, organizations can access development tools, middleware, and database management systems hosted in the cloud, enabling faster time-to-market for applications, improved collaboration among development teams, and reduced operational overhead.
Software-as-a-Service
Software as a Service (SaaS) can be defined as a software minus licenses and maintenance hassle. Businesses tend to subscribe the software on a monthly or yearly subscription basis (there might also be a few providers who give the offering for free, in return of an access to your usage data) and use it in their process by integrating with their internal systems.
Enterprises that choose to go with SaaS usually have to partner with a software vendor who uses third-party cloud provider for hosting the software. Or they can go with a brand like Microsoft or Amazon where the cloud provider are also software vendors. Some of the top SaaS providers in the industry are – Salesforce, HubSpot, and Adobe.
The SaaS provider you choose to work with will handle application access, along with the security and system performance. This means your business’s SaaS application would run on the providers’ servers, with no dependency on you to install or update software on-premises.
The use cases of SaaS model can include –
- Customer relationship management
- Human resource management
- Content management system
- Collaboration and communication
When to use SaaS
Software as a Service (SaaS) is invaluable for businesses seeking to access software applications over the internet without the need for installation or maintenance. SaaS providers deliver a wide range of applications, from productivity tools like email and office suites to enterprise resource planning (ERP) and customer relationship management (CRM) software, enabling organizations to increase operational efficiency, reduce IT overhead, and focus on core business activities.
Network-as-a-Service
Network as a Service (NaaS) is a software solution which merges IaaS with security and network solutions such as load balancing and unified threat management (UTM). For a startup who is new in the business, you can choose NaaS for its benefits that revolve around simplification of IT processes, automation of network management, and advanced security offering.
Companies can also benefit from NaaS through the functionality which enables them to let go of the complex headaches associated with networking, along with reduction of the operating expenses (OpEx) linked to hardware, network licenses, software, and the management tools.
NaaS is deemed ideal for businesses struggling with continuous capital costs, shortage of skills, and the growing complexities of remote access for employees. The managed wifi system also help with handling multiple cloud environments, while providing a reliable and secure private network for secure data transfer and reduced bottlenecks and latency.
Use cases of NaaS can include –
- Support remote work
- Store-as-a-Service
- Bandwidth-on-demand.
When to use NaaS?
Network as a Service (NaaS) offers businesses a cost-effective solution for managing their network infrastructure. NaaS providers offer scalable and customizable networking services, including VPNs, SD-WAN, and security features, allowing businesses to optimize their network performance, enhance connectivity, and ensure seamless communication across geographically dispersed locations.
Here was a complete rundown of the four popular and slightly confusing terms that are becoming mainstream in the digital space. We hope that you now have clarity in terms of deciding which model would be the best choice for your business.